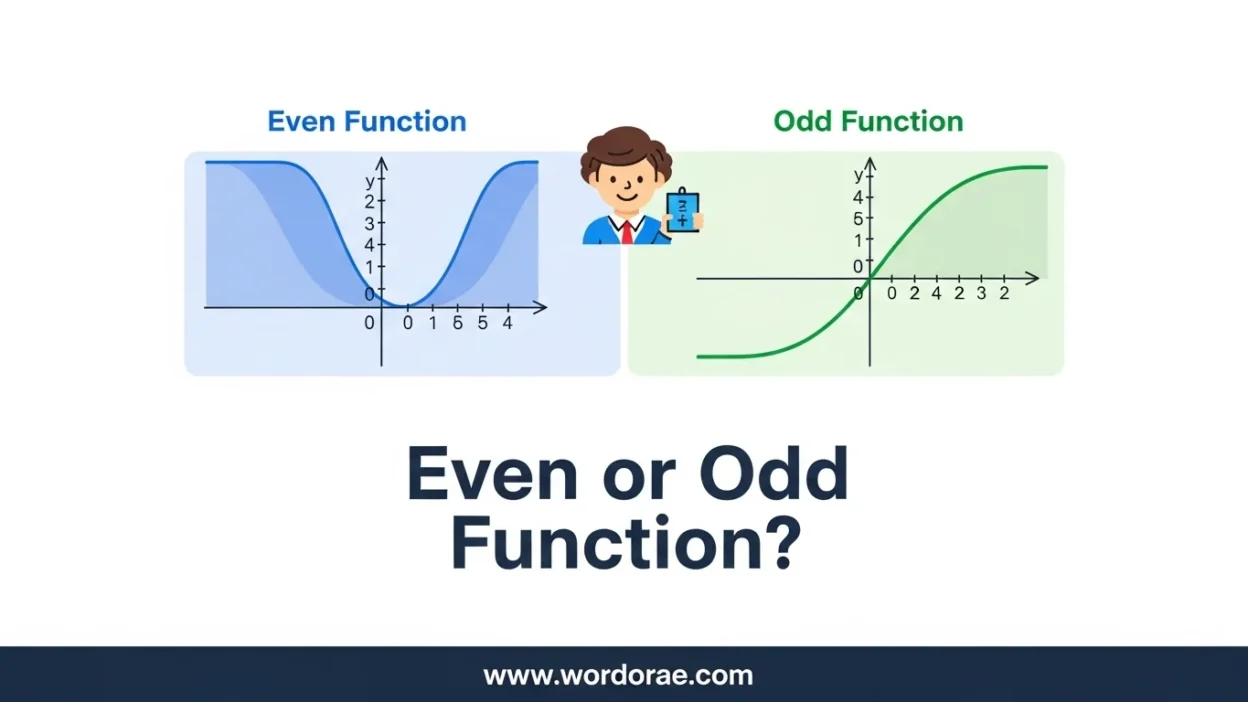
Quick answer: An even function satisfies f(−x) = f(x), while an odd function satisfies f(−x) = −f(x).
If you’ve ever studied math and stopped at the terms even function or odd function, you’re not alone.
I know this topic can feel confusing at first especially since the words “even” and “odd” make you think of numbers, not functions.
You might be wondering what these terms actually mean and how you’re supposed to tell them apart.
That’s exactly why I wrote this guide for you. I’ll break it down in plain language,
Walk you through simple rules that actually stick, and show you examples that make sense. No heavy formulas, no complicated math jargon.
By the end of this article, you’ll be able to identify an even or odd function quickly and confidently, whether you’re studying for an exam,
Helping a student, or just brushing up on your math basics. Plus, I’ll share some tips on avoiding common mistakes,
And real-life applications, so you can see why these concepts matter beyond textbooks.
Even or Odd Function – Quick Answer
- Even function: remains unchanged when x is replaced with −x → symmetric about the y-axis
- Odd function: changes sign when x is replaced with −x → symmetric about the origin
In simpler words: if a function mirrors perfectly across the y-axis, it’s even.
If rotating the graph 180° around the origin gives the same shape, it’s odd. Easy to remember once you visualize it!
The Origin of Even and Odd Functions
The idea of even and odd functions comes from mathematical symmetry.
Mathematicians noticed that some functions behave the same on both sides of the graph, while others flip predictably.
The terms even and odd were borrowed from numbers because:
- Even functions behave evenly on both sides
- Odd functions show an opposite relationship
These concepts became essential in algebra, calculus, physics, and engineering.
Recognizing symmetry can simplify problems, reduce computation, and even make integration faster in calculus.
So, this isn’t just abstract math, it has practical uses in science and technology.
Even vs Odd Function Rules
| Function Type | Rule | What It Means |
| Even function | f(−x) = f(x) | Same output for x and −x |
| Odd function | f(−x) = −f(x) | Output changes sign |
If a function satisfies neither rule, it is neither even nor odd. Knowing this helps avoid overthinking and keeps your work precise.
How to Identify an Even or Odd Function
Here’s a simple method you can use every time:
- Replace x with −x in the function.
- Simplify the expression.
- Compare it with the original function:
- Same expression → Even
- Negative of original → Odd
- Neither → Neither
This works for polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponentials, and more. The more examples you practice with, the faster this becomes second nature.
Common Examples of Even and Odd Functions
| Function | Type | Reason |
| f(x) = x² | Even | f(−x) = (−x)² = x² |
| f(x) = x³ | Odd | f(−x) = −x³ |
| cos(x) | Even | cos(−x) = cos(x) |
| sin(x) | Odd | sin(−x) = −sin(x) |
| f(x) = x⁴ − x² | Even | All powers even, mirror symmetry |
| f(x) = x⁵ + x³ | Odd | All powers odd, origin symmetry |
The more varied examples you see, the easier it is to recognize patterns and apply the rules quickly.
Graphical Meaning: Even vs Odd
Understanding the graph can make this topic much more intuitive.
Even Functions:
- Symmetric about the y-axis
- Left side mirrors the right side
Odd Functions:
- Symmetric about the origin
- Rotating the graph 180° gives the same graph
Neither:
- Some functions show no symmetry and are neither even nor odd.
Visualizing symmetry can help you check answers without doing heavy calculations.
Common Mistakes with Even and Odd Functions
- ❌ Thinking every function is either even or odd → ✅ Many functions are neither
- ❌ Forgetting to simplify after replacing x with −x → ✅ Always simplify fully first
- ❌ Confusing symmetry types → ✅ Y-axis symmetry = even, origin symmetry = odd
- ❌ Assuming all polynomials follow the pattern → ✅ Only those with all even or all odd powers fit
By keeping these in mind, you save time and avoid unnecessary confusion.
Even or Odd Function in Real Applications
Even and odd functions are more than just theory they appear in real life:
- Physics: wave motion, harmonic oscillations
- Engineering: analyzing circuits and systems
- Calculus: simplifying integrals and series expansions
- Computer graphics: calculating mirror symmetry and patterns
- Signal processing: decomposing signals into even and odd components
Recognizing symmetry can reduce complex problems into simpler, solvable pieces. That’s why engineers, scientists, and mathematicians use these concepts daily.
FAQs
Can a function be both even and odd?
Yes, but only the zero function (f(x) = 0).
Is every polynomial even or odd?
No. Only polynomials with all even or all odd powers qualify.
Is f(x) = x an odd function?
Yes, because f(−x) = −x.
Is f(x) = x² + x odd or even?
Neither.
Do even and odd functions matter in calculus?
Yes, they simplify limits, integrals, and series expansions.
Can trigonometric functions be even or odd?
Yes. Cos(x) is even, sin(x) is odd, and combinations follow rules based on their components.
Final Thoughts
Even and odd functions may seem tricky at first, but once you understand the rules, they become simple and intuitive.
An even function stays the same when you flip the sign of x, while an odd function flips its output. Recognizing these patterns helps you:
- Visualize symmetry in graphs
- Simplify calculations in calculus and physics
- Solve real-world problems more efficiently
Remember: y-axis symmetry = even, origin symmetry = odd. Practice a few examples, and soon identifying even and odd functions will feel automatic.

I’m Jane Austen, a writer at Wordorae.com, where I focus on explaining grammar mistakes and confusing English words in a clear, simple way.
I help readers improve their writing by making tricky language rules easy to understand and use.